1. 线程池
1.1. 使用线程池的好处
- 降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
- 提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要的等到线程创建就能立即执行。
- 提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
1.2. 如何创建线程池
Java通过Executors创建线程池的几种方式
- newCachedThreadPool:创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。
- newFixedThreadPool:创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
- newScheduledThreadPool:创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行
- newSingleThreadExecutor: 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
- new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAX_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.MINUTES, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(QUEUE_CAPACITY), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()):推荐使用ThreadPoolExecutor方法创建线程池。
1.3. Executors 返回线程池对象的弊端如下
- FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadExecutor : 允许请求的队列长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,可能堆积大量的请求,从而导致 OOM。
- CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool : 允许创建的线程数量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,可能会创建大量线程,从而导致 OOM。
1.4. 线程池参数详解
- int corePoolSize: 线程池的核心线程数
- int maximumPoolSize:线程池的最大线程数
- long keepAliveTime:当线程闲置时,保持线程存活的时间,默认情况下,只有当线程池中的线程数大于corePoolSize时,keepAliveTime才会起作用,直到线程池中的线程数不大于corePoolSize,即当线程池中的线程数大于corePoolSize时,如果一个线程空闲的时间达到keepAliveTime,则会终止,直到线程池中的线程数不超过corePoolSize
- TimeUnit unit:keepAliveTime的时间单位
- ThreadFactory threadFactory:线程工厂
- BlockingQueue
workQueue: 用来储存等待执行任务的队列 - RejectedExecutionHandler handler:拒绝策略
1.5. 线程池的拒绝策略
如果当前同时运行的线程数量达到最大线程数量并且队列也已经被放满了任时,ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 定义一些策略:
- ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy: 抛出 RejectedExecutionException来拒绝新任务的处理
- ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy: 调用执行自己的线程运行任务,也就是直接在调用execute方法的线程中运行(run)被拒绝的任务,如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务。因此这种策略会降低对于新任务提交速度,影响程序的整体性能。如果您的应用程序可以承受此延迟并且你要求任何一个任务请求都要被执行的话,你可以选择这个策略
- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy: 不处理新任务,直接丢弃掉
- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy: 此策略将丢弃最早的未处理的任务请求
1.6. 线程池执行关系
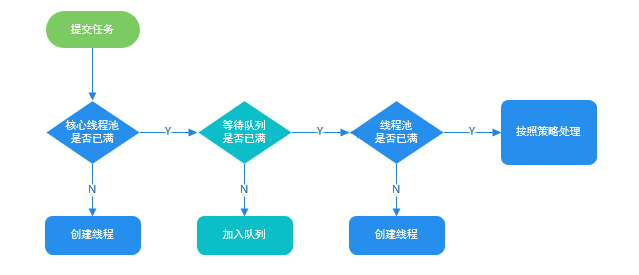
1.7. 使用方法:
public class ThreadUtil {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 10;
/**
* 任务队列
*/
private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 100;
/**
*当线程数大于核心时,多余的空闲线程等待新任务的存活时间。
*/
private static final Long KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 1L;
/**
* 缓存线程池方式
*/
private ExecutorService cacheThreadPool;
/**
* 定长线程池
*/
private ExecutorService fixedThreadPool;
/**
* 单线程化线程池
*/
private ExecutorService singleThreadPool;
/**
* 支持定时及周期性任务执行
*/
private ExecutorService scheduledThreadPool;
/**
* threadPoolExecutor方式创建线程池
*/
private ExecutorService threadPoolExecutor;
/**
* 单例获取线程池
* @return
*/
public static ThreadUtil getInstance(){
return ThreadPoolManagerHolder.instance;
}
private static class ThreadPoolManagerHolder {
public static ThreadUtil instance = new ThreadUtil();
}
private ThreadUtil(){
cacheThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAX_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,
TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(QUEUE_CAPACITY),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
}
public void executeTask(Runnable task){
threadPoolExecutor.execute(task);
}
public void cacheExecuteTask(Runnable task){
cacheThreadPool.execute(task);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
ThreadUtil.getInstance().executeTask(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
}
例子2:
public class ThreadLocalMain {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal =new ThreadLocal<>();
private ExecutorService executorService;
private ThreadLocalMain(){
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,10,1L, TimeUnit.MINUTES, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(20),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
}
public static ThreadLocalMain getInstance(){
return ThreadPoolManageHolder.instance;
}
private static class ThreadPoolManageHolder{
public static ThreadLocalMain instance = new ThreadLocalMain();
}
public void executorPool(Runnable task){
executorService.execute(task);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new ThreadLocalMain().execute();
}
public void execute() throws Exception{
threadLocal.set("测试threadLocal");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程中ThreadLocal的值:"+threadLocal.get());
ThreadLocalMain.getInstance().executorPool(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程中ThreadLocal的值:"+threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.set("测试2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"重新设置后线程中ThreadLocal的值:"+threadLocal.get());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程执行结束");
threadLocal.remove();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"remove后线程中ThreadLocal的值:"+threadLocal.get());
});
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程中ThreadLocal的值:"+threadLocal.get());
}
}
CountDownLatch实例
public class ThreadLocalMain {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal =new ThreadLocal<>();
private ExecutorService executorService;
private ThreadLocalMain(){
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,10,1L, TimeUnit.MINUTES, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(20),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
}
public static ThreadLocalMain getInstance(){
return ThreadPoolManageHolder.instance;
}
private static class ThreadPoolManageHolder{
public static ThreadLocalMain instance = new ThreadLocalMain();
}
public void executorPool(Runnable task){
executorService.execute(task);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new ThreadLocalMain().execute();
}
public void execute() throws Exception{
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
ThreadLocalMain.getInstance().executorPool(()->{
System.out.println("子线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始执行");
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("子线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完成");
latch.countDown();//当前线程调用此方法,则计数减一
});
}
System.out.println("主线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"等待子线程执行完成...");
latch.await();//阻塞当前线程,直到计数器的值为0
System.out.println("主线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始执行...");
}
}